Recently, the first round Radiative Electron Capture (REC) experiment was accomplished at HIRFL-CSRe internal target by Prof. CAI Xiaohong's group. This is the first on-line internal-target experiment at CSRe, and also the first REC experiment of Xe54+ with gaseous target collisions which marked a new milestone of HIRFL-CSR facility.
HIRFL-CSR project means that the Cooler-Storage-Ring project, the post-acceleration system of the Heavy Ion Research Facility in Lanzhou (HIRFL), it consists of a main ring (CSRm) and an experimental ring (CSRe).
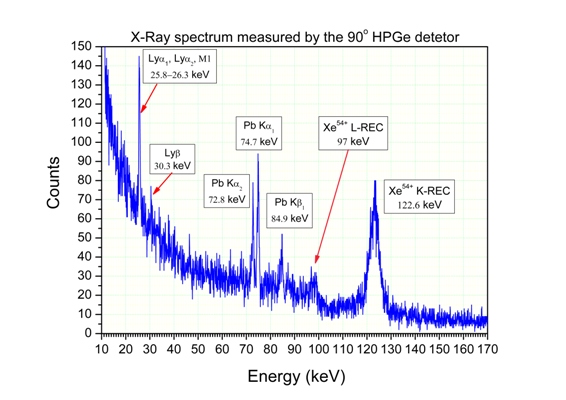
For the first time the Xe54+ beam was stored and electron-cooled at CSRe, and overlapped the internal target jet. In the experiment, the Xe27+ ion beam produced by a superconductor ECR ion source was firstly accelerated to 2.9 MeV/u by the SFC cyclotron, and was finally accelerated up to 200 MeV/u at CSRm. After that it was stripped by a 0.2 mm thick carbon foil to get the bare Xe54+ ions. The Xe54+ beam was injected into CSRe, and cooled by the hollow electron-beam cooler. While the beam was crossing with the N2 internal target jet, the REC X-rays were measured by three HPGe detectors, at 90°, 120° and 145°, respectively. The storage lifetime of Xe54+ in CSRe was also measured both with and without the electron cooler. The beam momentum spread was as small as DP/P≈2.2×10-5. During the experiment, the target thickness kept stable, and the remote control system of the internal target worked well. The experiment layout and feasibility, as well as the long-term stability of the CSRe internal target have been verified.
|

