Researchers of the Centre for Green Chemistry and Catalysis, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP), CAS, reported the N-alkylation of sulfonamide by a practical copper catalyst via a hydrogen borrowing mechanism. The simple Cu (OAc)2/ K2CO3 system allows for a benign alkylation of sulfonamides with alcohols in good to excellent yields. Mechanistic studies proved the transfer hydrogenation mechanism and C-H cleavage as the rate-determining step.
A full report of the study entitled “Copper-Catalyzed N-Alkylation of Sulfonamides with Benzylic Alcohols: Catalysis and Mechanistic Studies” was published in the recent issue of Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis (Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 2949–2958).
Nitrogen-containing compounds are of significant importance as building blocks for pharmaceuticals and novel bio-active compounds. Though versatile catalytic procedures for carbon-nitrogen (C-N) bond formation have been developed, further improvements are still possible. With respect to alkylated amides, N-alkylated sulfonamides constitute an important class of compounds. However, the existing preparation methods of alkylated sulfonamides all have certain disadvantages, such as the storage and handling problems resulted from the usage of sulfonyl chlorides, the generation of unwanted inorganic salts, etc. As for the recent research on the catalytic N-alkylation of sulfonamides with alcohols in the presence of ruthenium catalysts, though alcohols are readily available, non-expensive, and non-toxic, the use of such noble metal catalysts is limited due to their high price and the indispensable need of stabilizing ligands.
The current study demonstrated for the first time that the alkylation of sulfonamides with alcohol proceeds in the presence of easily available copper acetate via hydrogen borrowing methodology.
Abstract of the paper published in Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis
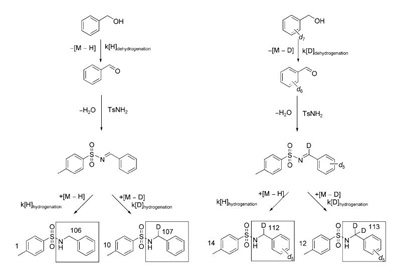
An illustration of the kinetic studies by isotope competitive reactions |

