A facile approach to fabricate solid-phase microextraction(SPME) fiber of perpendicularly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays in situ on Ti wire substrates using the anodization method was reported (Journal of Chromatography A 1217 (12): 1898-1903) by the researchers of the Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwestern Plant Resources, CAS. The fibers thus fabricated are metal-based, unbreakable fibers with new coatings that have high sensitivity/selectivity for target analytes.
The novel SPME fiber coupled with GC is then used to extract polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs), alkanes, phenols and anilines from water samples, and exhibits many advantages over commercial SPME fibers, including high rigidity, long service life, good stability at high temperature and in acid and alkali solutions, large surface areas (high adsoptivity), good selectivity for PAHs, wide linear range and low limit of detection(LODs) for extracting PAHs, simple preparation, and cost-effectiveness. The method represents a key addition to the family of SPME fibers, and has strong application potentials in the high-efficient and selective extraction of PAHs at trace levels from complex samples.
Recently, a new extraction technology, SPME, is being developed and has attracted considerable attentions due to its attractive properties and wide applications.The core part of SPME technique is the SPME fiber consisting of a substrate fiber and a coating as a stationary phase to adsorb the analytes from samples. However, almost all commercially available and new-type SPME substrate fibers are prepared with fused-silica, which is fragile and must be handled with great care, thus greatly limits the service life. Besides, many polymer coatings having a number of drawbacks are commercially applied to extract many organic compounds.
With the new method reported, on one hand, the Ti metal wire instead of the friable fused-silica wire is adopted as the fiber substrate, which can provide high strength, and prolong the service life. On the other hand, perpendicularly orientated and well-aligned TiO2 nanotube coating is successfully fabricated in situ on the Ti fiber substrate and used as the adsorptive phase. This unique nano-textured structure can greatly improve the surface area, and thus increase the enrichment effect.
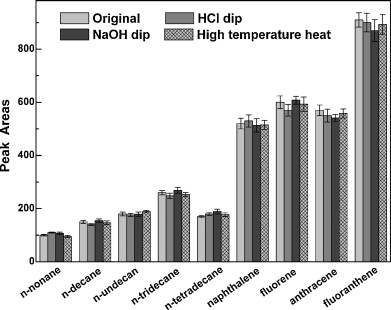
Comparison of the chromatographic peak area of PAHs and alkanes before and after dipping the tip of the fiber into acid, basic solutions for 48 h, and treating it at high temperature (350 °C) for 10 h (n = 3). |

