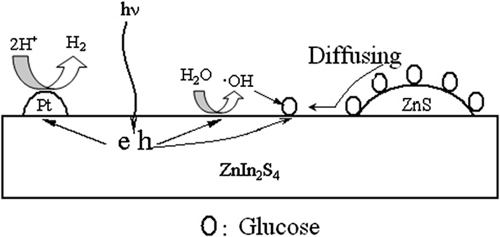
The schematic illustration of the mechanism of photocatalytic hydrogen evolution over ZnS–ZnIn2S4 in the presence of glucose.
Researchers at the State Key Laboratory for Oxo Synthesis and Selective Oxidation of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP) of the CAS have studied the photocatalytic hydrogen generation in the presence of glucose over ZnS-coated ZnIn2S4 under visible light irradiation. They first prepared ZnS-coated ZnIn2S4 photocatalysts with hexagonal crystal phase in methanol by a facile solvothermal process. The photocatalysts have complex morphology such as microspheres, micro-tubes and micro-ribbons, which depends on amount of ZnS of ZnS(x mol%)–ZnIn2S4.
Using glucose as electron donor, photocatalytic hydrogen generation is promoted greatly over Pt/ZnS (17mol%)–ZnIn2S4 with simultaneous degradation of glucose. The prepared ZnS (xmol%)–ZnIn2S4 photocatalysts exhibit better activity for hydrogen generation than pure ZnIn2S4, which may be attributed to the fact that ZnS on the ZnIn2S4 improves the adsorption of glucose. The effect of glucose concentration on the hydrogen generation rate is consistent with a Langmuir model. The basic condition is favorable for the photocatalytic hydrogen generation, and the optimal NaOH concentration is 0.12 mol-1. A large number of·OH radicals, which played an important role in visible photocatalytic activity of ZnS–ZnIn2S4 system, have been tested by the TA-FL method.
The work is significant for the renewable hydrogen production through Photocatalytic water splitting by solar light.
It has received support from the National Nature Science Foundation of China, National Basic Research Program of China, Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi, China, and Research Fund of Education Ministry of Jiangxi, China.
The findings have been published in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy (International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 35 (2010) 7116–7126).
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy Paper

