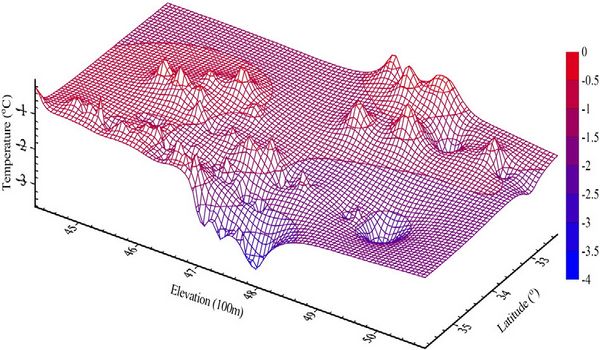
(Variations of permafrost temperatures at 15 m depth with elevation and latitude along the Qinghai-Tibetan Highway/Railway)(image/Global and Planetary Change)
The research of Permafrost temperatures and thickness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau was finished recently by the researcher of Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute.The accomplishment of the research has the important significance to describe the thermal state of permafrost along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway/Railway.
Based on permafrost temperature measurements from 190 boreholes along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway/Railway since the early 1960s, the researcher present spatial variations of permafrost temperatures, thermal gradients,and thickness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Overall, permafrost temperatures at 15 m depth are higher than −4.0 °C and about half of the permafrost has its temperature higher than −1.0 °C. The lowest average permafrost temperature is about −3.8 °C in the Fenghuo Mts. area. Permafrost temperatures are strongly controlled by elevation and latitude on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Permafrost temperatures at 15 m depth decrease at a rate of 0.57 °C per 100 m altitude increase and 0.79 °C per latitude moving north. Permafrost temperature gradients change dramatically along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway/Railway, ranging from about 1.0 °C/100 m in Liangdaohe basin of southern Plateau to 8.0 °C/100 m in Kunlun Mts. area of northern Plateau. Assuming thermal conductivity of 2.0 Wm−1 °C−1 of bedrocks at depth, geothermal heat flux varies from 0.02 Wm−2 to 0.16 Wm−2. Permafrost thickness ranges from less than 10 m to over 300 m along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway/Railway. Besides elevation and latitude, geothermal heat flux also plays a key role in controlling permafrost temperature and thickness.
The research was subsidized by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 40625004); the grant of the Western Project Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. KZCX2-XB2-
10; the China Meteorological Administration Research Project (GYHY(QX)2007-6-18).

