The researchers in Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMP) have investigated the correlation between alpha-decay energies of superheavy nuclei (SHN) and the effect of symmetry energy on the isospin dependence of the Qαvalues of SHN along an alpha-decay chain. A new approach has been proposed for predicting the Qαvalues of SHN and a simple formula has been got for describing the correlation between the a-decay energies of SHN,
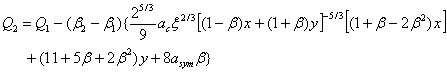
By using the proposed approach, the Qαvalues of SHN have been calculated and the results are given by the marked and hollow rectangles in Fig.1 in comparison with the experimental values (shaded area). It is seen that except for 294118, 290115, 282113 and 280111, the new approach can reproduce the measured values accurately with a root-mean-square deviation 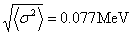 and an average deviation
and an average deviation 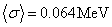 for centralvalues from 380 reference-target combinations. The calculated Qαvalues of 294118, 282113 and 280111 are lower than the experimental ones, which is possibly attributed to the likely proton and neutron shell gaps at Z=120 and at N=166, respectively. The resulting satisfactory agreement between the experimental and theoretical Qαvalues implies that the proposed approach is able to predict the Qαvalues of SHN accurately and since the Qαvalues of the reference nuclei are taken from the experimental measurements, the agreement suggests that the experimental data themselves are consistent with each other, which indicates that the experimental observations and measurements of the SHN are reliable to a great extent. Most importantly, a proton number of Z = 114 and a neutron number of N = 172 turn out to be not shell closures for the present synthesized SHN.
for centralvalues from 380 reference-target combinations. The calculated Qαvalues of 294118, 282113 and 280111 are lower than the experimental ones, which is possibly attributed to the likely proton and neutron shell gaps at Z=120 and at N=166, respectively. The resulting satisfactory agreement between the experimental and theoretical Qαvalues implies that the proposed approach is able to predict the Qαvalues of SHN accurately and since the Qαvalues of the reference nuclei are taken from the experimental measurements, the agreement suggests that the experimental data themselves are consistent with each other, which indicates that the experimental observations and measurements of the SHN are reliable to a great extent. Most importantly, a proton number of Z = 114 and a neutron number of N = 172 turn out to be not shell closures for the present synthesized SHN.
The effect of symmetry energy on the stability of SHN against a decay is also discussed. By using the proposed approach, the effect of symmetry energy on the isospin dependence of the Qαvalues of SHN along isotope chains has been studied and the results are reported in Fig.2. It is found that the experimentally observed increase of alpha-decay half-lives with increasing neutron number, i.e., the increased stability of these SHN against alpha-decay with larger neutron number, is primarily attributed to the effect of the symmetry energy.
The work has been published in Phys. Rev. Lett.107, 012501 (2011).
The article can be linked as follows: http://prl.aps.org/pdf/PRL/v107/i1/e012501

Fig. 1 Comparison of the predicted Qα values of SHN (the rectangles with error bars) and the experimental ones (shaded area) of recently synthesized heaviest SHN. The horizontal ordinate denotes the mass numbers of the reference nuclei(Image by IMP).
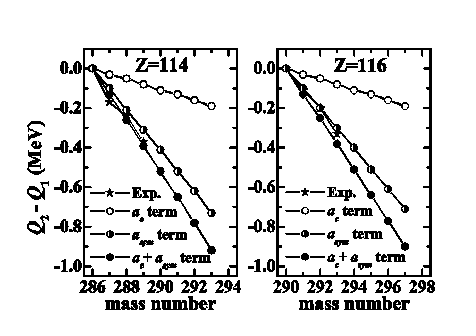
Fig. 2 Effect of symmetry energy on Q2-Q1 by taking the elements 114 and 116 as examples (286114 and 290116 as reference nuclei with α-decay energies Q1, respectively).The experimental data, if available, are also shown forcomparison(Image by IMP).

