The tensor force is a hot topic in nuclear physics. It affects the shell evolution and some important issues of nuclear structure, and it plays an important role in the investigation of exotic nuclei and superheavy nuclei.
A detailed investigation for the effect of the tensor force on the pseudospin energy splitting has been carried out taking the Sn isotope chain as an example in the framework of the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock approach with the Sly5+TF and T31+TF parameter sets combined with the BCS method. Part of the results is reported in Fig.1. The tensor force turns out to obviously affect the pseudospin energy splitting of the spin-unsaturated nuclei. The contributions of the tensor force to the pseudospin symmetry are significant since all pseudospin doublets except (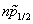 ,
,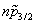 ) are composed of a j> orbit and a j< orbit which are affected in an opposite way by the tensor force. For (
) are composed of a j> orbit and a j< orbit which are affected in an opposite way by the tensor force. For (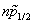 ,
,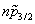 ), only the
), only the 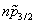 orbit is shifted due to the tensor force, and hence the tensor force also affects the pseudospin splitting. Since the tensor force shifts the single-particle levels, it modifies the single-particle level density and the shell correction energy.
orbit is shifted due to the tensor force, and hence the tensor force also affects the pseudospin splitting. Since the tensor force shifts the single-particle levels, it modifies the single-particle level density and the shell correction energy.
The effect of the tensor force on the shell correction energy has also been studied. It is shown that the tensor force influences the shell correction energy considerably (see Fig.2). For the superheavy nucleus 298114, it is found that the shell gap at Z = 114 is obviously enlarged due to the tensor force but the shell gap at N = 184 is changed only slightly by adopting the present parameter sets. This may explain the fact that nearly all of modern calculations predict the existence of a closed neutron shell at N = 184 while large divergence in predicting the position of the closed proton shell. In other words, many-body approaches with various parameter sets tend to predict different locations of the shell gaps, which perhaps results from the uncompleted knowledge about the tensor force to a large extent.
The work has been published in Physical Review C84, 014303 (2011). The paper can be found on the webpage: http://prc.aps.org/pdf/PRC/v84/i1/e014303.
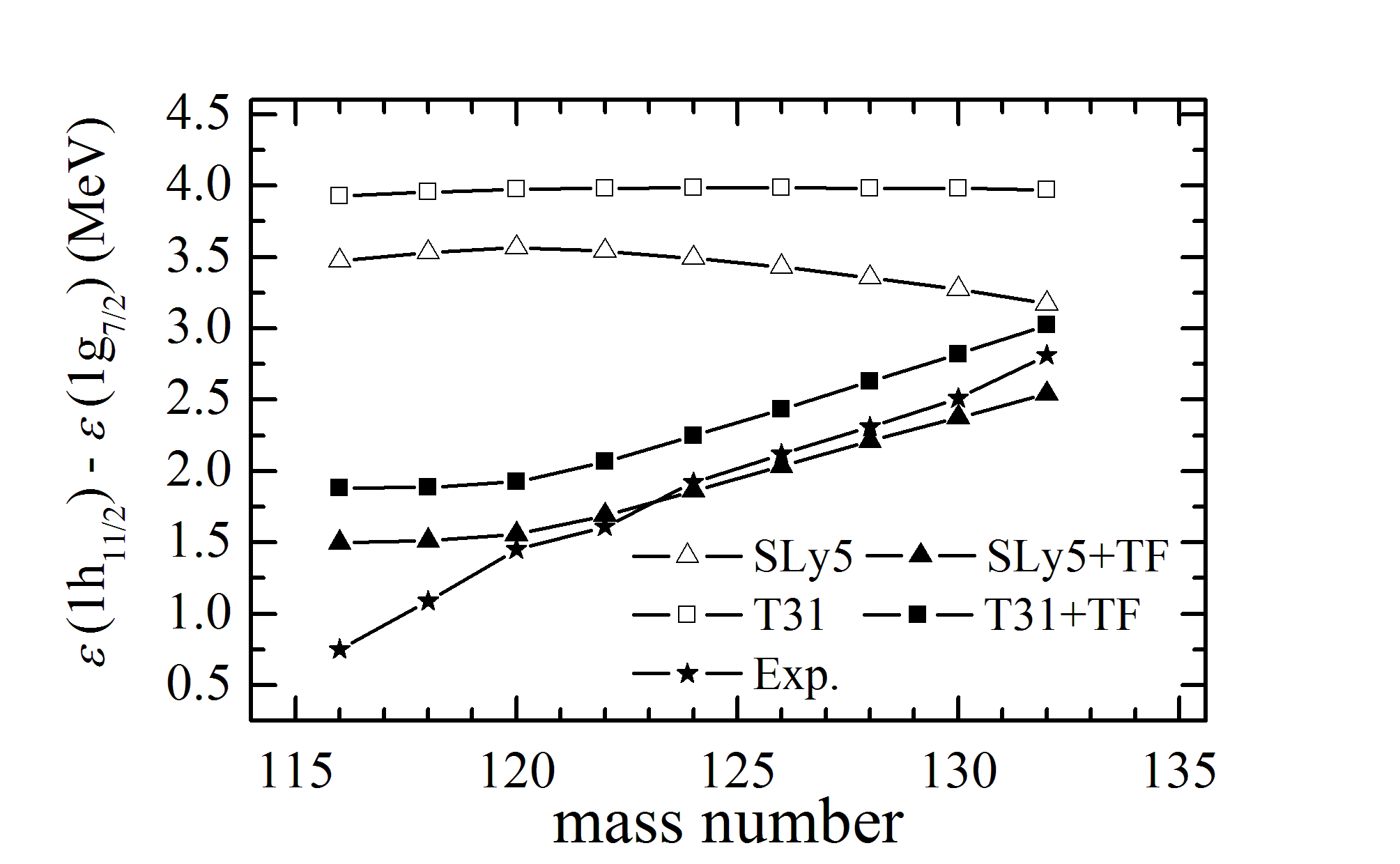
FIG.1 Energy differences between the 1h11/2 and 1g7/2 single-proton states along the Sn isotopes.(Image by IMP)
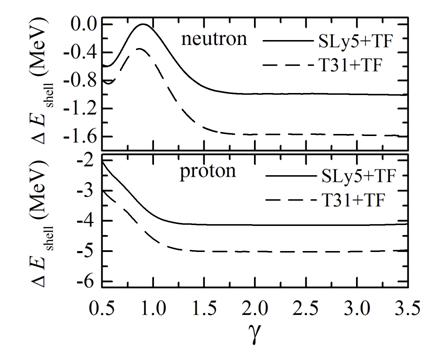
FIG.2 Modification of neutron and proton shell correction energies due to the tensor force as a function of the smoothing range γ for 298114. (Image by IMP)

