Magnetic monopoles arise as exact solutions of varies gauge field theories, as the spontaneously broken Yang–Mills–Higgs theory, grant unified field theory, electroweak theory etc. Recently, a new "magnificent seventh" detector in LHC at CERN, MoEDAL, was finished and plan to collect data of magnetic monopoles and other exotic particles. Therefore, theoretical study of monopoles becomes more and more important and interesting.
Researchers in Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMP) and their collaborators from Warwick University and Tours University studied the topology structure and instability of monopoles.
By exploring the stability problem of non-Abelian monopoles. Researchers found that the so-called "Brandt–Neri–Coleman type" variations of monopoles can be reduced to a pure gauge theory on the two-sphere. Each topological sector admits exactly one stable monopole charge, and each unstable monopole admits 2∑(2|q|−1) negative modes, where the sum goes over the negative eigenvalues q of an operator related to the non-Abelian charge Q of Goddard, Nuyts and Olive. These results are useful for those experimenters to search monopoles in their laboratory.
The work has been published in: Ann. Phys. 327 (2012) 118
The papers can be found in the following link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003491611001412
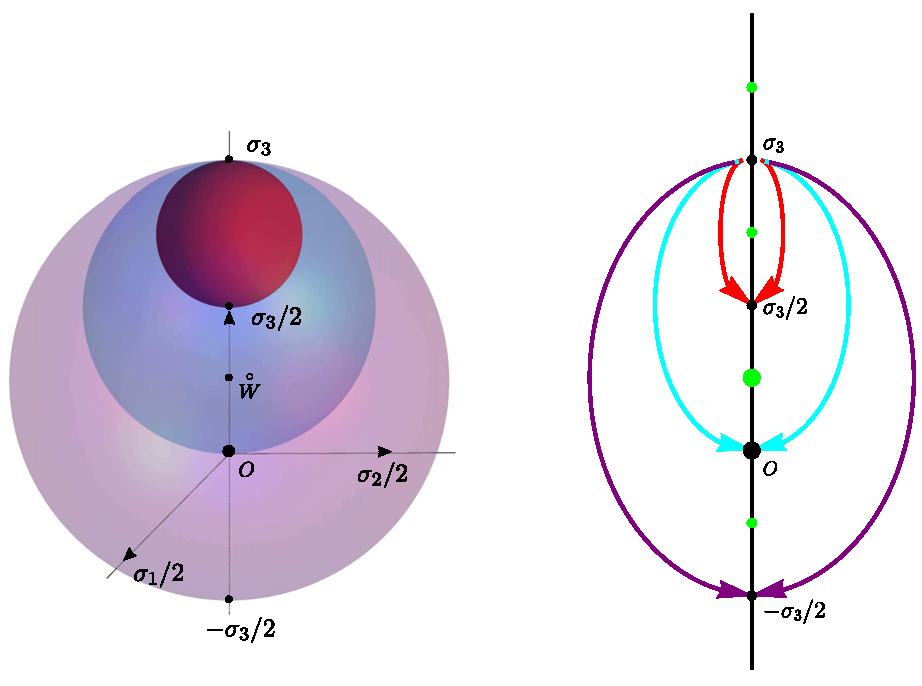
Fig.1 The SU(2) monopole with GNO charge Q = \sigma_3 has 6 negative modes.(Imaged by IMP)

