In order to find the change law of uniaxial compression strength and failure strain of freezing salty silt under the influence of water content, natural saline soil was collected from the shore side of the Yellow River in Pingchuan district of Baiyin Municipality of Gansu Province as the sample. After leaching with distilled water, the soil was used to prepare specimens containing NaCl/Na2SO4 at salt content of 1.5% with different water contents. Analytically pure sodium sulfate and sodium chloride are used in the test. The test results indicate that when the water content was low, as the water content increasing, cementing power of ice increases, at the same time, ice endure more and more load with soil particles and crystals of salt, so the uniaxial compression strength of frozen salty soil will increase. When the water content increases to a certain degree, ice plays a leading role in the soil, the specimen presents the properties of ice, and the compression strength of ice is far less than that of mineral grains, so the uniaxial compression strength of frozen salty silt will decrease when the water content is over a given value. Failure strain has the similar change law with uniaxial compression strength changing with water content.
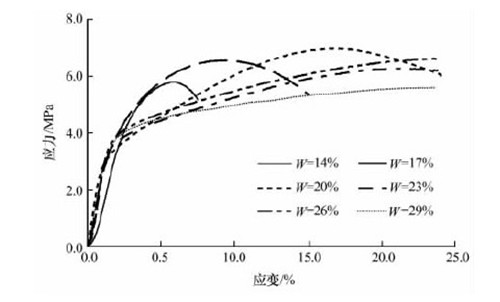
The stress-strain curves for frozen silt containing Na2SO4 for different water contents
The stress-strain curves for frozen silt containing NaCl for different water contents |

