The study of halo nuclei has been a subject of great interest in recent decades. The striking feature of halo nuclei is the long tail of their matter density due to their weak binding energies. It has been found that the elastic scattering, a simple process, is a useful probe to study the size and surface diffuseness of exotic nuclei by comparing similarities and differences in reactions induced by weakly-bound and tightly-bound nuclei.
Researchers from Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMP) experimentally explored the elastic scattering in proton drip-line nucleus 8B off a heavy target.
The elastic scattering of 8B on a heavy target, natPb, was measured at incident energy of 170.3 MeV. The 8B secondary beam was produced by the Radioactive Ion Beam Line in Lanzhou (RIBLL). Special care was taken with the limited intensity and broad profile of the secondary beam. The disadvantages of broad beam profiles and limited intensities of the RIBs were overcome by using large area detectors, two Parallel-Plate Avalanche Counters (PPACs), two double-sided silicon strip detector (DSSD) telescopes, incorporated with Monte Carlo simulations. The method is suitable for the measurement of the cross sections on heavy targets at low and intermediate energies.
The measured angular distribution of the differential cross section shows that the Coulomb-nuclear interference peak (CNIP) is not suppressed in this system, in contrast to what was observed in the scattering of neutron halo nuclei on heavy targets at energies around the Coulomb barrier. Analyses of the angular distribution were performed both in terms of the optical model and the Continuum Discretized Coupled Channels (CDCC) method, which explicitly takes into account the breakup channel couplings to the elastic scattering. The overall pattern of the differential cross section is well reproduced by the CDCC calculations. In spite of its very low breakup threshold (0.1375 MeV), the results show that the effect of breakup-channel couplings on the elastic scattering is small in the present case. The present data make an important contribution to the property study of the drip-line nucleus the 8B.
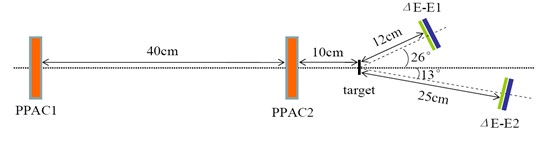
Fig.1 Schematic view of experimental setup (Image by IMP)
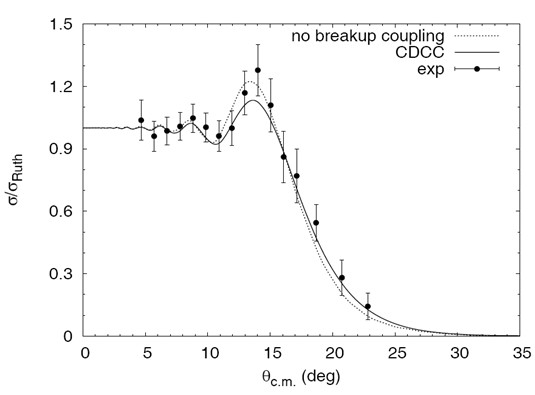
Fig.2 Comparison between CDCC calculations and experimental data for 170.3 MeV 8B+natPb elastic scattering (Image by IMP)

