Microorganisms are a primary life form in low-temperature environments.They are deposited in glaciers through atmospheric circulation and precipitation.Glacier microorganisms can influence surface albedo and the hydrochemistry of precipitation,and serve as primary producers in material cycles and energy flows of glaciers.The community structure and diversity of culturable microorganisms in ice cores and snow pits have been studied by traditional culture methods .However,it is estimated that only 1% of the microorganisms in environmental samples can be isolated,So accurate environmental microbial study is hampered. Therefore,since the mid 1980s,many microbiologists have investigated the amount,community structure,and function of environmental microorganisms by culture-independent methods,such as molecular hybridization,electrophoresis(denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis,DGGE;and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis,TGGE),high-throughput sequencing,and so on,but their uses in the study of environmental microorganisms are based on the high DNA yield and quality.
DNA extraction of environmental microorganisms involves sample pretreatment,cell lysis (physical lysis,chemical lysis,and the combining of different lysis patterns), and extraction,DNA. Many biotechnology companies have produced various DNA extraction kits for environmental microorganisms.Compared with traditional extraction methods,using DNA extraction kits is time- and labor-saving,making them suitable for extracting DNA from scores of microbial samples.However,DNA extraction kits are expensive,so their application is limited.To date,there is no single DNA extraction method suitable for all environmental microbial samples.The biomass of glacier microorganisms is low and Gram-positive bacteria are the dominant group,so it is very difficult to establish a high-quality DNA extraction method.This paper reports on certain optimized DNA extraction methods and compares them with a typical commercial kit,and makes recommendations for their use in the study of glacier microorganisms.
In order to thoroughly investigate the diversity of glacier microorganisms,four DNA extraction methods with different lysis patterns were tested and two screened methods were optimized for the most effective form of the filter membrane (cut vs. uncut),the DNA extraction method, and the precipitation method.The two optimized methods were then compared with the commercial Mo-Bio DNA extraction kit,and the results showed that the kit was generally suitable for extraction of microorganism DNA from glacier surface snow.Procedurally,it was found that a modified Bosshard-Bano method (i.e., cutting the filter membrane into pieces, using a specific lysis pattern [lysozyme (5 mg/mL)-protease K(1 mg/mL)-CTAB (1%)-SDS (1%)], performing the extraction only once by chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (24:1),and conducting DNA precipitation by pure ethanol) was also an effective and less expensive method for extraction of microorganism DNA from glacier surface snow.
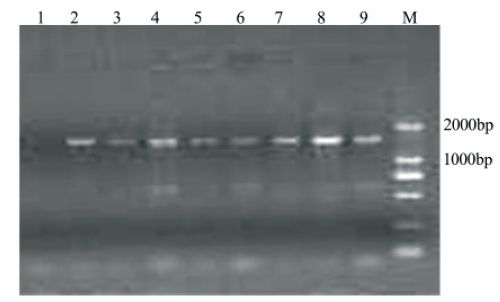
Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR amplified 16S
rDNA gene of bacteria from glacier surface snow by three methods.
1–3: ZH (Zhou) method; 4–6: ZE (modified Bosshard-Bano)
method; 7–9: Kit method. Model DL2000 DNA Marker
(ShineGene Molecular Biotech, Inc., Shanghai, China)
Download from the attachment

