Researchers in the Theoretical Physics Group at Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMP) investigated the 3PF2 pairing in pure neutron matter in collaboration with Prof. Lombardo of Catania University and INFN-LNS, Italy.
The effects of the Fermi surface depletion (Z-factor) have been included in the calculation of the energy gap. In the pure degenerate limit, the 3PF2 superfluid phase extends over a broad density range with a gap peak value of about 0.2 MeV without 3BF and 0.5 MeV with 3BF. The inclusion of Z-factor leads to a rapid decrease of the gap magnitude by one order of magnitude: its peak value drops to less than 0.05 MeV and the superfluidity domain shrinks to 0.1-0.4 fm−3. In neutron stars, the proton fraction in β-equilibrium with neutrons could, in principle, affect the 3PF2 pairing, but in the non-vanishing gap range it is less than 15% of total density. Recent calculations on the isospin dependence of the quasi-particle strength show that the enhancement of the neutron Z-factor is negligible for such small proton fraction. Even including the additional screening suppression, the conclusion remains that the departure from the Fermi gas limit is the main cause of pairing disappearance in high-density nuclear matter.
The present result is expected to be important for the cooling properties of neutron stars and it makes doubtful the role of the 3PF2 pairing in neutron star core.
The work has been published in Phys. Rec. C as rapid Communication.
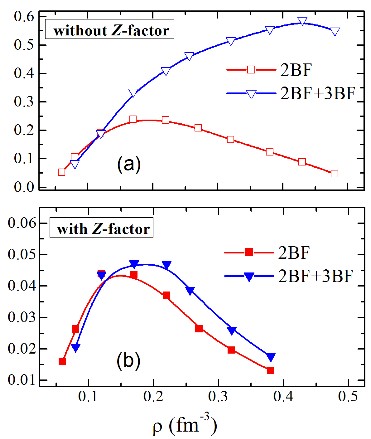
Fig. 1 3PF2 pairing gaps in pure neutron matter. (Image by IMP)

