Telomeres are highly repetitive sequences on chromosome, locate at the ends of chromosomes structure, which play an important role in the maintenance and protection. Telomere shortening and abnormal changes could result in cellular senescence and death. Since telomeres in normal cells with inactivated telomerase become shorter each cell division; while in tumor cells as abnormal activation of telomerase activity, telomere length which may not be shortened as cell division. This is an important mechanism for tumor cells to maintain its proliferative potential.
In the study, researchers found that after heavy ion irradiation, despite the rapid DNA damage in MCF-7 and HeLa cells can be repaired, but still ultimately went to cell death. Through inhibition of DNA double-strand break repair system non-homologous end joining, it was found that DNA damage was still to get a quick fix, but the cell radiosensitivity was greatly enhanced. Further analysis indicated that this might be due to inhibition of DNA-PKcs telomerase induced protection status change. Current data suggested that DNA-PKcs inhibition could enhance cellular sensitivity to carbon-ion radiation via disturbing its functional role in telomere end protection. The combination of DNA-PKcs inhibition and carbon-ion irradiation may be an efficient method of heavy-ion therapy.
Findings were published in Plos One, 8 (8): e72641 (2013).
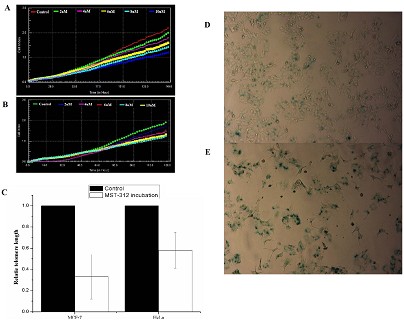
Tumor cells with shorter telomere showed higher radiosensitivity. (Image by IMP)

