Recently researchers in the Radiation Medicine Group at the Institute of Modern Physics(IMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences obtained new findings on Pseudo-Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (PMMP) triggered autophagy via proton displacement with exogenous positive charges.
The mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound organelle. Protein complexes in the inner membrane transfer protons (H+), and the incremental production of energy is used to pump protons back into the intermembrane space. A strong electrochemical gradient (Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, MMP) is established across the inner membrane as the proton concentration increases in the intermembrane space. Protons can return to the matrix through the ATP synthase complex, and their potential energy is used to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. Therefore, the MMP is used to maintain the cellular energy supply, which is essential for normal physiological processes.
Researchers in Radiation Medicine Group found that MitoQ is adsorbed to the inner mitochondrial membrane; however, its cationic moiety remains in the intermembrane space, resulting in the addition of a large number of positive charges to protons. The balance of MMP was maintained by MitoQ attenuating the activity of respiratory chain complexes I, III, and IV (which are associated with proton generation) and decreasing the proton pumping rate. Furthermore, the positive charges in MitoQ replaced protons in the establishment of the electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane. This distinct MMP could not maintain a normal energy supply and therefore was designated “pseudo-MMP” (PMMP).
The positive charges in MitoQ replaced protons in the establishment of the electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane. In this instance, protons backflow was severely impaired, resulting in the decreased production of ATP, blocked mitochondrial respiratory function and impaired energy metabolism via induction of PMMP. Starvation induced autophagy via the AMPK-MTOR signal pathway.
This study is the first to hypothesize about PMMP and helped elucidate the mechanisms used by lipophilic cation drugs to induce PMMP. It is also the first to prove the new mechanisms of autophagy via proton displacement with exogenous positive charges.
This study was jointly supported by the NSFC-CAS Joint Fund for Research Based on Large-scaled Scientific Facilities, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Western Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The research achievements have been published in Autophagy, 2017, 13(4): 1–9 (DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1280219) and the article link is as follows:
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/15548627.2017.1280219
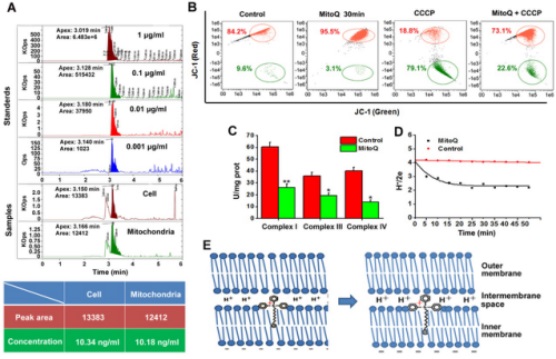
Fig.1 Construction of pseudo-mitochondrial membrane potential (PMMP) by MitoQ

Fig.2 Effects of PMMP induced by MitoQ on energy metabolism and autophagy

