Soil salinization is one of the main causes of land degradation in arid and semi-arid areas. It is an important basis to reveal the degree and spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinization. Based on the topsoil salinity data of Minqin irrigated areas, the spatial variability and distribution characteristics of the topsoil salinity and ions were studied by the method of classical statistics and geostatistics. The results showed that topsoil salinity of the study areas was mainly composed of Na+ and SO42-. The content of Cl- and HCO3- showed moderate variation characteristics, while the total salt and other salt ions content showed strong variability. The total salt and all salt ions showed a strong spatial correlation, and the spatial autocorrelation distance was 4.62-11.13 km, which indicated that the total salt and all salt ions had great similarity in the spatial autocorrelation. The distribution trends of total salt, Ca2+, Mg2+, CL- and SO42- were higher consistent, the low value areas were concentrated in southwest and north centra region, high value areas were mainly distributed in the middle areas, northeast and northwest areas of the irrigation area. The research results have been published in the Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment in an article entitled “Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Topsoil Salinity in the Minqin Oasis, Northwest China.” This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Yong Talent Growth Foundation of CAREERI. 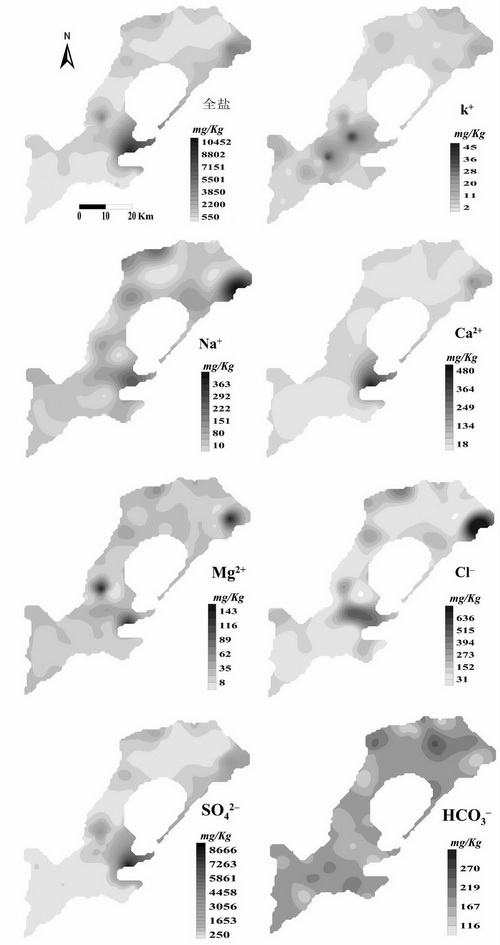
Kriging interpolation distribution map of topsoil salinity and ions content |

